08-15-2020, 04:18 PM
Former Illinois Governor James Thompson
James Robert Thompson Jr. (May 8, 1936 – August 14, 2020), also known as Big Jim Thompson, was the 37th and longest-serving governor of the US state of Illinois,[1] serving from 1977 to 1991. A Republican, Thompson was elected to four consecutive terms and held the office for 14 years. Many years after leaving public office, he served as a member of the National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States (the 9/11 Commission).
Thompson was born in Chicago, Illinois, the son of Agnes Josephine (Swanson) and James Robert Thompson, a physician. His maternal grandparents were Swedish.[3] Thompson graduated from North Park Academy (now North Park University), studied at the University of Illinois at Chicago Navy Pier campus, and at Washington University in St. Louis. He received his J.D. from Northwestern University in 1959.[citation needed]
Prior to becoming governor, he worked in the Cook County state's attorney's office, taught at Northwestern University's law school and was appointed by President Nixon to serve as U.S. Attorney for the Northern District of Illinois. As a federal prosecutor in the early 1970s, he obtained a conviction against former Governor Otto Kerner, Jr., for his use of improper influence on behalf of the racetrack industry.[citation needed]
He tried and convicted many of Chicago Mayor Richard J. Daley's top aides, most notably Alderman Thomas E. Keane and County Clerk Matt Danaher, on various corruption charges. People like Keane and Danaher, the mayor's point man on patronage were also major figures in the Cook County Democratic Party's political machine. These high-profile cases gave Thompson the celebrity that fueled his run for governor in 1976.[citation needed]
To the chagrin of many, Thompson was bipartisan in his attacks on corruption in Cook County and Chicago. He not only prosecuted high-profile Democrats, but also prominent Republicans such as County Commissioner Floyd Fulle and former U.S. Senate candidate, William Rentschler. Organized crime in Chicago was harder for his unit to crack and there were few high-profile cases during his era.[citation needed]
In the 1976 election, he won 65 percent of the vote over Democratic Secretary of State Michael Howlett, who had defeated incumbent Governor Dan Walker in the primary and who had the support of Chicago Mayor and Cook County Democratic Party chairman Richard J. Daley. Thompson was the first candidate for governor to receive over 3 million votes; his tally of 3,000,395 remains the largest number of votes ever cast for a candidate in an election for Governor of Illinois. His first term was for only two years because Illinois moved its gubernatorial election from presidential-election years to midterm-election years. Thompson was re-elected to a full four-year term in 1978 with 60 percent of the vote, defeating State Comptroller Michael Bakalis. In 1982, Thompson was very narrowly re-elected over former U.S. Senator Adlai E. Stevenson III. Thompson won the contest by only 5,074 votes.[4] A rematch in 1986 was expected to be almost as close, but the Democrats were severely hamstrung when supporters of Lyndon LaRouche won the Democratic nominations for lieutenant governor and secretary of state. Stevenson refused to appear on the same ticket as the LaRouchites, and formed the Solidarity Party with the support of the regular state Democratic organization. With the Democrats badly split, Thompson skated to victory in the general election. Thompson was accused of hiding the sad shape that Illinois' economy and budget were in while campaigning, but once elected, called for an emergency session of the Illinois legislature to address the crisis.[citation needed]
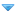
![[Image: 220px-Illinois_Governor_James_R._Thompso...y_1986.jpg]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/87/Illinois_Governor_James_R._Thompson_observing_Operation_Haylift%2C_July_1986.jpg/220px-Illinois_Governor_James_R._Thompson_observing_Operation_Haylift%2C_July_1986.jpg)
On November 12, 1980, Thompson, by his executive order, instituted a hiring freeze for all state agencies, boards, bureaus, and commissions under his control as governor. The order affected approximately 60,000 state positions.[[url=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Citation_needed]citation needed]
These positions could only be filled if the candidates were first approved by an office created by Thompson, the Governor's Office of Personnel. Suit was brought and the Supreme Court held this political patronage practice unconstitutional as a violation of the First Amendment rights of low-level public employees in Rutan v. Republican Party of Illinois, 497 U.S. 62 (1990).
In 1989, Governor Thompson agreed to establish a compounding, 3 percent cost-of-living increase for retirees from Illinois government jobs, including public school teachers. Years later, in an interview with a Chicago business magazine, Thompson said he never knew the cost might exceed $1 billion and likely would not have signed it if he had known.[5] In recent years, the cumulative effect of the 3 percent annual increases has been recognized as one of the major causes of Illinois' public employee pension crisis.
In 1993, the State of Illinois Center in Chicago was renamed the James R. Thompson Center to honor the former governor.[6]
James Robert Thompson Jr. (May 8, 1936 – August 14, 2020), also known as Big Jim Thompson, was the 37th and longest-serving governor of the US state of Illinois,[1] serving from 1977 to 1991. A Republican, Thompson was elected to four consecutive terms and held the office for 14 years. Many years after leaving public office, he served as a member of the National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States (the 9/11 Commission).
Thompson was born in Chicago, Illinois, the son of Agnes Josephine (Swanson) and James Robert Thompson, a physician. His maternal grandparents were Swedish.[3] Thompson graduated from North Park Academy (now North Park University), studied at the University of Illinois at Chicago Navy Pier campus, and at Washington University in St. Louis. He received his J.D. from Northwestern University in 1959.[citation needed]
Prior to becoming governor, he worked in the Cook County state's attorney's office, taught at Northwestern University's law school and was appointed by President Nixon to serve as U.S. Attorney for the Northern District of Illinois. As a federal prosecutor in the early 1970s, he obtained a conviction against former Governor Otto Kerner, Jr., for his use of improper influence on behalf of the racetrack industry.[citation needed]
He tried and convicted many of Chicago Mayor Richard J. Daley's top aides, most notably Alderman Thomas E. Keane and County Clerk Matt Danaher, on various corruption charges. People like Keane and Danaher, the mayor's point man on patronage were also major figures in the Cook County Democratic Party's political machine. These high-profile cases gave Thompson the celebrity that fueled his run for governor in 1976.[citation needed]
To the chagrin of many, Thompson was bipartisan in his attacks on corruption in Cook County and Chicago. He not only prosecuted high-profile Democrats, but also prominent Republicans such as County Commissioner Floyd Fulle and former U.S. Senate candidate, William Rentschler. Organized crime in Chicago was harder for his unit to crack and there were few high-profile cases during his era.[citation needed]
In the 1976 election, he won 65 percent of the vote over Democratic Secretary of State Michael Howlett, who had defeated incumbent Governor Dan Walker in the primary and who had the support of Chicago Mayor and Cook County Democratic Party chairman Richard J. Daley. Thompson was the first candidate for governor to receive over 3 million votes; his tally of 3,000,395 remains the largest number of votes ever cast for a candidate in an election for Governor of Illinois. His first term was for only two years because Illinois moved its gubernatorial election from presidential-election years to midterm-election years. Thompson was re-elected to a full four-year term in 1978 with 60 percent of the vote, defeating State Comptroller Michael Bakalis. In 1982, Thompson was very narrowly re-elected over former U.S. Senator Adlai E. Stevenson III. Thompson won the contest by only 5,074 votes.[4] A rematch in 1986 was expected to be almost as close, but the Democrats were severely hamstrung when supporters of Lyndon LaRouche won the Democratic nominations for lieutenant governor and secretary of state. Stevenson refused to appear on the same ticket as the LaRouchites, and formed the Solidarity Party with the support of the regular state Democratic organization. With the Democrats badly split, Thompson skated to victory in the general election. Thompson was accused of hiding the sad shape that Illinois' economy and budget were in while campaigning, but once elected, called for an emergency session of the Illinois legislature to address the crisis.[citation needed]
![[Image: 220px-Illinois_Governor_James_R._Thompso...y_1986.jpg]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/87/Illinois_Governor_James_R._Thompson_observing_Operation_Haylift%2C_July_1986.jpg/220px-Illinois_Governor_James_R._Thompson_observing_Operation_Haylift%2C_July_1986.jpg)
On November 12, 1980, Thompson, by his executive order, instituted a hiring freeze for all state agencies, boards, bureaus, and commissions under his control as governor. The order affected approximately 60,000 state positions.[[url=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Citation_needed]citation needed]
These positions could only be filled if the candidates were first approved by an office created by Thompson, the Governor's Office of Personnel. Suit was brought and the Supreme Court held this political patronage practice unconstitutional as a violation of the First Amendment rights of low-level public employees in Rutan v. Republican Party of Illinois, 497 U.S. 62 (1990).
In 1989, Governor Thompson agreed to establish a compounding, 3 percent cost-of-living increase for retirees from Illinois government jobs, including public school teachers. Years later, in an interview with a Chicago business magazine, Thompson said he never knew the cost might exceed $1 billion and likely would not have signed it if he had known.[5] In recent years, the cumulative effect of the 3 percent annual increases has been recognized as one of the major causes of Illinois' public employee pension crisis.
In 1993, the State of Illinois Center in Chicago was renamed the James R. Thompson Center to honor the former governor.[6]
The ideal subject of totalitarian rule is not the convinced Nazi or the dedicated Communist but instead the people for whom the distinction between fact and fiction, true and false, no longer exists -- Hannah Arendt.