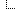07-09-2021, 08:12 AM
Former First Lady of Egypt, Jehan Sadat
Jehan Sadat[1] (Arabic: جيهان السادات Jihān as-Sadāt,[2] [ʒeˈhæn es.sæˈdæːt]; née Safwat Raouf; 29 August 1933 – 9 July 2021[3]) was an Egyptian human rights activist the widow of Anwar Sadat, and the First Lady of Egypt from 1970 until her husband's assassination in 1981. As Egypt's first lady, she greatly influenced the reform of the country's civil rights legislation. Advance laws, referred to as the "Jihan Laws", have given women in Egypt a range of new rights, such as the right to child support and custody in the event of divorce.
Jehan Sadat, also spelled Jihan, was born Jehan Safwat Raouf (Arabic: جيهان صفوت رؤوف Jīhān Ṣafwat Raʼūf [ʒeˈhæːn ˈsˤɑfwɑt ɾɑˈʔuːf]) in Cairo, Egypt, as the first girl and third child of an upper-middle-class family of an Egyptian surgeon father, Safwat Raouf, and English music teacher mother, Gladys Cotterill. Her mother was the daughter of Charles Henry Cotterill, a Sheffield City police superintendent. She was raised as a Muslim, according to her father's wishes, but also attended a Christian secondary school for girls in Cairo.
As a teenage schoolgirl, she was intrigued by Anwar Sadat as a local hero, through following reports in the media about his adventures, in addition to his courage, loyalty, and determination in resisting the British occupation of Egypt. She heard many stories about him from her cousin, whose husband was his colleague in resistance, and later in prison.
It was at her 15th birthday party that she first met her future husband Sadat, shortly after his release from prison,[4] where he had served two and a half years for his political activities.
The couple married on 29 May 1949, after some hesitation, and objections from her parents to the idea of their daughter marrying a jobless revolutionary. He was 30, while she was 15. Anwar Sadat was subsequently part of the core members of the Free Officers Movement that led the Egyptian Revolution of 1952, which overthrew the monarchy of Egypt and Sudan.
]
![[Image: lossy-page1-220px-Jimmy_Carter%2C_Presid...61.tif.jpg]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8d/Jimmy_Carter%2C_President_of_Egypt_Anwar_Sadat%2C_Rosalynn_Carter_and_Mrs._Jihan_Sadat._-_NARA_-_174261.tif/lossy-page1-220px-Jimmy_Carter%2C_President_of_Egypt_Anwar_Sadat%2C_Rosalynn_Carter_and_Mrs._Jihan_Sadat._-_NARA_-_174261.tif.jpg)
Over the course of 32 years, Sadat was a supportive wife for her husband, who, in his rising political career, who would go on to become President of Egypt. The couple had three daughters, Noha, Jihan, Lobna, and a son, Gamal.
Sadat became First Lady of Egypt in 1970, and used her platform to touch the lives of millions inside her country, serving as a role model for women everywhere. She helped change the world's image of Arab women during the 1970s, while undertaking volunteer work, and participating in non-governmental service to the less fortunate.[citation needed]
Sadat played a key role in reforming Egypt's civil rights laws during the late 1970s. Often called "Jehan's Laws", new statutes advanced by her granted women a variety of new rights, including those to alimony and custody of children in the event of divorce.
After visiting wounded soldiers at the Suez front during the Six-Day War in 1967, she founded al Wafa' Wa Amal (Faith and Hope) Rehabilitation Center, which offers disabled war veterans medical and rehabilitation services and vocational training. The center is supported by donations from around the world and now serves visually impaired children and has a worldwide known music and choir band.
She also played crucial roles in the formation of the Talla Society, a cooperative in the Nile Delta region which assists local women in becoming self-sufficient , the Egyptian Society for Cancer Patients, the Egyptian Blood Bank, and SOS Children's Villages in Egypt, an organization that provides orphans new homes in a family environment.
She headed the Egyptian delegation to the UN International Women's Conferences in Mexico City and Copenhagen. She founded the Arab-African Women's League. As an activist, she hosted and participated in numerous conferences throughout the world concerning women's issues, children's welfare, and peace in Africa, Asia, Europe, and North and South America.
On 6 October 1981, Sadat's husband was assassinated by members of the Egyptian Islamic Jihad during the annual victory parade held in Cairo to celebrate Operation Badr. This ended both his presidency and her period as First Lady, which had endured for nearly 11 years.
Education[edit]
Sadat gained a BA in Arabic Literature at Cairo University in 1977. This was followed by a MA in Comparative Literature in 1980, and PhD in Comparative Literature in 1986, both at the same university.
After completing her education, Sadat became a teacher at the Cairo Artist and Performance Center.
![[Image: 220px-JehanSadat.jpg]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/JehanSadat.jpg/220px-JehanSadat.jpg)
Jehan Sadat speaks at the Dean Lesher Regional Center for the Arts in [url=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Walnut_Creek,_California]Walnut Creek, California, on 11 April 2006
Sadat was a Senior fellow at the University of Maryland, College Park (where The Anwar Sadat Chair for Peace and Development has also been endowed).
She also wrote an autobiography, A Woman of Egypt (ISBN 0-7432-3708-0), published by Simon & Schuster in 1987, as well as poetry in Arabic, under a pseudonym. Her second memoir, My Hope for Peace, was released in March 2009.
Jehan Sadat died on July 9. 2021 at the age of 87. Prior to her death she had reportedly been battling cancer.[5]
Sadat was the recipient of several national and international awards for public service and humanitarian efforts for women and children. She also received more than 20 honorary doctorate degrees from national and international colleges and universities around the world. In 1993, she received the Community of Christ International Peace Award, whilst in 2001, she was the winner of the Pearl S. Buck Award. After her death, Egyptian President Abdel Fattah El Sisi issued a decree awarding her the Order of Perfection.[6] It was also announced that the Al-Firdous axis (Axis of Paradise) in Cairo will be named after her.[6]
Jehan Sadat[1] (Arabic: جيهان السادات Jihān as-Sadāt,[2] [ʒeˈhæn es.sæˈdæːt]; née Safwat Raouf; 29 August 1933 – 9 July 2021[3]) was an Egyptian human rights activist the widow of Anwar Sadat, and the First Lady of Egypt from 1970 until her husband's assassination in 1981. As Egypt's first lady, she greatly influenced the reform of the country's civil rights legislation. Advance laws, referred to as the "Jihan Laws", have given women in Egypt a range of new rights, such as the right to child support and custody in the event of divorce.
Jehan Sadat, also spelled Jihan, was born Jehan Safwat Raouf (Arabic: جيهان صفوت رؤوف Jīhān Ṣafwat Raʼūf [ʒeˈhæːn ˈsˤɑfwɑt ɾɑˈʔuːf]) in Cairo, Egypt, as the first girl and third child of an upper-middle-class family of an Egyptian surgeon father, Safwat Raouf, and English music teacher mother, Gladys Cotterill. Her mother was the daughter of Charles Henry Cotterill, a Sheffield City police superintendent. She was raised as a Muslim, according to her father's wishes, but also attended a Christian secondary school for girls in Cairo.
As a teenage schoolgirl, she was intrigued by Anwar Sadat as a local hero, through following reports in the media about his adventures, in addition to his courage, loyalty, and determination in resisting the British occupation of Egypt. She heard many stories about him from her cousin, whose husband was his colleague in resistance, and later in prison.
It was at her 15th birthday party that she first met her future husband Sadat, shortly after his release from prison,[4] where he had served two and a half years for his political activities.
The couple married on 29 May 1949, after some hesitation, and objections from her parents to the idea of their daughter marrying a jobless revolutionary. He was 30, while she was 15. Anwar Sadat was subsequently part of the core members of the Free Officers Movement that led the Egyptian Revolution of 1952, which overthrew the monarchy of Egypt and Sudan.
]
![[Image: lossy-page1-220px-Jimmy_Carter%2C_Presid...61.tif.jpg]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8d/Jimmy_Carter%2C_President_of_Egypt_Anwar_Sadat%2C_Rosalynn_Carter_and_Mrs._Jihan_Sadat._-_NARA_-_174261.tif/lossy-page1-220px-Jimmy_Carter%2C_President_of_Egypt_Anwar_Sadat%2C_Rosalynn_Carter_and_Mrs._Jihan_Sadat._-_NARA_-_174261.tif.jpg)
[/url]
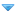
The Sadats with US president Jimmy Carter and his wife Rosalyn in 1977
The Sadats with US president Jimmy Carter and his wife Rosalyn in 1977
Over the course of 32 years, Sadat was a supportive wife for her husband, who, in his rising political career, who would go on to become President of Egypt. The couple had three daughters, Noha, Jihan, Lobna, and a son, Gamal.
Sadat became First Lady of Egypt in 1970, and used her platform to touch the lives of millions inside her country, serving as a role model for women everywhere. She helped change the world's image of Arab women during the 1970s, while undertaking volunteer work, and participating in non-governmental service to the less fortunate.[citation needed]
Sadat played a key role in reforming Egypt's civil rights laws during the late 1970s. Often called "Jehan's Laws", new statutes advanced by her granted women a variety of new rights, including those to alimony and custody of children in the event of divorce.
After visiting wounded soldiers at the Suez front during the Six-Day War in 1967, she founded al Wafa' Wa Amal (Faith and Hope) Rehabilitation Center, which offers disabled war veterans medical and rehabilitation services and vocational training. The center is supported by donations from around the world and now serves visually impaired children and has a worldwide known music and choir band.
She also played crucial roles in the formation of the Talla Society, a cooperative in the Nile Delta region which assists local women in becoming self-sufficient , the Egyptian Society for Cancer Patients, the Egyptian Blood Bank, and SOS Children's Villages in Egypt, an organization that provides orphans new homes in a family environment.
She headed the Egyptian delegation to the UN International Women's Conferences in Mexico City and Copenhagen. She founded the Arab-African Women's League. As an activist, she hosted and participated in numerous conferences throughout the world concerning women's issues, children's welfare, and peace in Africa, Asia, Europe, and North and South America.
On 6 October 1981, Sadat's husband was assassinated by members of the Egyptian Islamic Jihad during the annual victory parade held in Cairo to celebrate Operation Badr. This ended both his presidency and her period as First Lady, which had endured for nearly 11 years.
Education[edit]
Sadat gained a BA in Arabic Literature at Cairo University in 1977. This was followed by a MA in Comparative Literature in 1980, and PhD in Comparative Literature in 1986, both at the same university.
After completing her education, Sadat became a teacher at the Cairo Artist and Performance Center.
![[Image: 220px-JehanSadat.jpg]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/JehanSadat.jpg/220px-JehanSadat.jpg)
Jehan Sadat speaks at the Dean Lesher Regional Center for the Arts in [url=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Walnut_Creek,_California]Walnut Creek, California, on 11 April 2006
Sadat was a Senior fellow at the University of Maryland, College Park (where The Anwar Sadat Chair for Peace and Development has also been endowed).
She also wrote an autobiography, A Woman of Egypt (ISBN 0-7432-3708-0), published by Simon & Schuster in 1987, as well as poetry in Arabic, under a pseudonym. Her second memoir, My Hope for Peace, was released in March 2009.
Jehan Sadat died on July 9. 2021 at the age of 87. Prior to her death she had reportedly been battling cancer.[5]
Sadat was the recipient of several national and international awards for public service and humanitarian efforts for women and children. She also received more than 20 honorary doctorate degrees from national and international colleges and universities around the world. In 1993, she received the Community of Christ International Peace Award, whilst in 2001, she was the winner of the Pearl S. Buck Award. After her death, Egyptian President Abdel Fattah El Sisi issued a decree awarding her the Order of Perfection.[6] It was also announced that the Al-Firdous axis (Axis of Paradise) in Cairo will be named after her.[6]
The ideal subject of totalitarian rule is not the convinced Nazi or the dedicated Communist but instead the people for whom the distinction between fact and fiction, true and false, no longer exists -- Hannah Arendt.